12.A - 숫자 포맷 예외처리
DESCRIPTION
숫자가 아닌 문자가 피연산자로 들어 왔을 때, 그 정보를 제공하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
올바른 표현 : 숫자 op(+, -, *, /, %) 숫자
INPUT
Line 1 : N ( 문장의 개수 N = 1 ~ 1000)
Line 2 ~ N+1 : 공백으로 구분된 3개의 단어 (차례대로 숫자, op, 숫자)
- 단어의 길이는 2을 넘지 않음
OUTPUT
Line 1 ~ N : 올바른 문장이면 계산 결과를 출력
올바르지 않은 문장은 "Wrong Input: 올바르지 않은 문자열" 출력 (cf, 피연산자 두개 모두 올바르지 않을 때, 앞에 꺼 출력)
SAMPLE INPUT
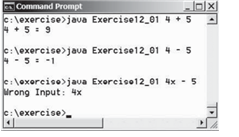
3
4 + 5
4 - 5
4x – 5
SAMPLE OUTPUT
4 + 5 = 9
4 - 5 = -1
Wrong Input: 4x
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt(), i, j;
input.nextLine();
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
String s = input.nextLine();
String sc[] = new String[3];
int a, b;
boolean check = true, checkint = false;
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++){
sc[j] = s.split(" ")[j];
}
for(j = 0; j < sc[0].length(); j++){
if((sc[0].charAt(0)+"").compareTo("-") == 0){
checkint = true;
continue;
}
if(Character.isDigit(sc[0].charAt(j)) == false){
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[0]);
check = false;
}
}
if(!check)
continue;
a = checkint == false ? Integer.parseInt(sc[0]) : -(Integer.parseInt(sc[0].substring(1,sc[0].length())));
checkint = false;
for(j = 0; j < sc[2].length(); j++){
if((sc[2].charAt(0)+"").compareTo("-") == 0){
checkint = true;
continue;
}
if(Character.isDigit(sc[2].charAt(j)) == false){
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[2]);
check = false;
}
}
if(!check)
continue;
b = checkint == false ? Integer.parseInt(sc[2]) : -(Integer.parseInt(sc[2].substring(1,sc[2].length())));
if(check){
if(sc[1].compareTo("+") == 0)
System.out.println(a + " + " + b + " = " + (a + b));
else if(sc[1].compareTo("-") == 0)
System.out.println(a + " - " + b + " = " + (a - b));
else if(sc[1].compareTo("*") == 0)
System.out.println(a + " * " + b + " = " + a * b);
else if(sc[1].compareTo("/") == 0){
if(b == 0)
System.out.println("Wrong Input: 0");
else
System.out.println(a + " / " + b + " = " + a / b);
}
else if(sc[1].compareTo("%") == 0)
if(b == 0)
System.out.println("Wrong Input: 0");
else
System.out.println(a + " % " + b + " = " + a % b);
else
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[1]);
}
}
}
}
Wrong Answer 0
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt(), i, j;
input.nextLine();
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
String s = input.nextLine();
String sc[] = new String[3];
boolean check = true;
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++){
sc[j] = s.split(" ")[j];
}
for(j = 0; j < sc[0].length(); j++){
if(Character.isDigit(sc[0].charAt(j)) == false){
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[0]);
check = false;
}
}
if(!check)
continue;
for(j = 0; j < sc[2].length(); j++){
if(Character.isDigit(sc[2].charAt(j)) == false){
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[2]);
check = false;
}
}
if(check){
if(sc[1].compareTo("+") == 0)
System.out.println(sc[0] + " + " + sc[2] + " = " + (Integer.parseInt(sc[0]) + Integer.parseInt(sc[2])));
else if(sc[1].compareTo("-") == 0)
System.out.println(sc[0] + " - " + sc[2] + " = " + (Integer.parseInt(sc[0]) - Integer.parseInt(sc[2])));
else if(sc[1].compareTo("*") == 0)
System.out.println(sc[0] + " * " + sc[2] + " = " + Integer.parseInt(sc[0]) * Integer.parseInt(sc[2]));
else if(sc[1].compareTo("/") == 0){
if(sc[2].compareTo("0") == 0)
System.out.println("Wrong Input: 0");
else
System.out.println(sc[0] + " / " + sc[2] + " = " + Integer.parseInt(sc[0]) / Integer.parseInt(sc[2]));
}
else if(sc[1].compareTo("%") == 0)
if(sc[2].compareTo("0") == 0)
System.out.println("Wrong Input: 0");
else
System.out.println(sc[0] + " % " + sc[2] + " = " + Integer.parseInt(sc[0]) % Integer.parseInt(sc[2]));
else
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[1]);
}
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt(), i, j;
input.nextLine();
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
String s = input.nextLine();
String sc[] = new String[3];
int a, b;
boolean check = true, checkint = false;
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++){
sc[j] = s.split(" ")[j];
}
for(j = 0; j < sc[0].length(); j++){
if((sc[0].charAt(0)+"").compareTo("-") == 0){
checkint = true;
continue;
}
if(Character.isDigit(sc[0].charAt(j)) == false){
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[0]);
check = false;
}
}
a = checkint == false ? Integer.parseInt(sc[0]) : -(Integer.parseInt(sc[0].substring(1,sc[0].length())));
checkint = false;
if(!check)
continue;
for(j = 0; j < sc[2].length(); j++){
if((sc[2].charAt(0)+"").compareTo("-") == 0){
checkint = true;
continue;
}
if(Character.isDigit(sc[2].charAt(j)) == false){
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[2]);
check = false;
}
}
b = checkint == false ? Integer.parseInt(sc[2]) : -(Integer.parseInt(sc[2].substring(1,sc[2].length())));
if(check){
if(sc[1].compareTo("+") == 0)
System.out.println(a + " + " + b + " = " + (a + b));
else if(sc[1].compareTo("-") == 0)
System.out.println(a + " - " + b + " = " + (a - b));
else if(sc[1].compareTo("*") == 0)
System.out.println(a + " * " + b + " = " + a * b);
else if(sc[1].compareTo("/") == 0){
if(b == 0)
System.out.println("Wrong Input: 0");
else
System.out.println(a + " / " + b + " = " + a / b);
}
else if(sc[1].compareTo("%") == 0)
if(b == 0)
System.out.println("Wrong Input: 0");
else
System.out.println(a + " % " + b + " = " + a % b);
else
System.out.println("Wrong Input: " + sc[1]);
}
}
}
}
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "4x"
at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580)
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:615)
at Main.main(Main.java:25)
12.B - 16진법 예외처리
Time Limit: 1s Memory Limit: 128MB
DESCRIPTION
Sample Code를 참고하여 입력 문자열이 16진법이 아니면 16진법 예외가 발생한 위치를 알려주는 프로그램을 구현하시오.
본 문제에서 사용하는 16진법은 아라비아 숫자와 알파벳 대문자(소문자는 예외처리)로만 표현된 숫자라고 가정한다. 0X, 0x 표기는 생략한다.
INPUT
Line 1 : 문자열의 개수 N
Line 2 ~ 1+N : 16진법이거나 아닌 문자열들
OUTPUT
Line 1 ~ N : 16진법이라면 10진수로 변환 /
16진법이 아니라면
HexFormatException: Illegal hex character: "16진법이 아닌 문자" 출력
SAMPLE CODE
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = sc.nextInt();
for (int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
String hex = sc.next();
int value;
try {
value = HexFormat.parseHex(hex);
} catch (HexFormatException ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
continue;
}
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}YOUR_CODE
SAMPLE INPUT
5
A5
FAA
T10
ABC
10.
SAMPLE OUTPUT
165
4010
HexFormatException: Illegal hex character: T
2748
HexFormatException: Illegal hex character: .
class HexFormat{
public static int parseHex(String s) throws HexFormatException{
int ans = 0, i;
char c;
for(i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
c = s.charAt(i);
ans *= 16;
if('0' <= c && c <= '9')
ans += c - '0';
else if('A' <= c && c <= 'F')
ans += 10 + c - 'A';
else
throw new HexFormatException(c);
}
return ans;
}
}
class HexFormatException extends Exception{
private String s = "HexFormatException: Illegal hex character: ";
public HexFormatException(char c){
this.s = s + c;
}
public String toString(){
return s;
}
}
12.C - Java 소스 코드 포맷팅
Time Limit: 1s Memory Limit: 128MB
DESCRIPTION
next-line brace style을 end-of-line brace style로 변환 하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
예를 들어, 다음 (a)의 Java code는 next-line brace style이고, (b)는 end-of-line brace style입니다.
여러분의 프로그램은 Java source code file로부터 Command line을 argument로 전달 받습니다.
그 Command line을 end-of-line brace style로 변환 해야 합니다.
Write a program that converts the Java source code from the next-line brace style to the end-of-line brace style.
For example, the following Java source in (a) uses the next-line brace style. Your program converts it to the end-of-line brace style in (b).
Your program can be invoked from the command line with the Java sourcecode file as the argument.
It converts the Java source code to a new format.
For example, the following command converts the Java source-code file Test.java to the end-of-line brace style.

INPUT
next-line brace style인 자바 소스코드
OUTPUT
end-of-line brace style인 자바 소스코드
SAMPLE INPUT
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("###");
}
}
SAMPLE OUTPUT
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("###");
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String s;
int i;
boolean pre = false, pre2 = false;
while(input.hasNextLine()){
s = input.nextLine();
if(s.contains("{")) {
System.out.print(" {");
pre = false;
}
else {
if(pre2)
System.out.println();
System.out.print(s);
pre = false;
pre2 = true;
}
}
}
}'학부공부 > Java_Basic' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter 18. Recursion(1)[Java Basic] (0) | 2021.11.06 |
|---|---|
| Chapter 13. Abstract Classes and Interfaces[Java Basic] (0) | 2021.11.06 |
| Chapter 11. Inheritance and Polymorphism[Java Basic] (0) | 2021.11.06 |
| Chapter 10. Object-Oriented Thinking(3)[Java Basic] (0) | 2021.11.06 |
| Chapter 10. Object-Oriented Thinking(2)[Java Basic] (0) | 2021.11.06 |



댓글